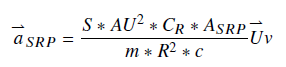By default, when Solar Radiation Pressure (SRP) is enabled in a Spacecraft's ForceModel, FreeFlyer uses a spherical model to calculate acceleration due to SRP. For the spherical model, the accelerations due to the force of the solar radiation pressure act in the direction away from the Sun, and therefore the effect is seen regardless of the Spacecraft's orientation, so long as the Spacecraft is not in shadow. The magnitude of the applied force is proportional to the mass, cross-sectional area normal to the direction to the Sun, the coefficient of reflectivity (CR) of the Spacecraft, and the inverse of the square of the distance from the Spacecraft to the Sun. These parameters provide flexibility in modeling the solar radiation pressure to match your mission's needs.
For the spherical model, the formula used to calculate the acceleration due to solar radiation pressure is:
|
(1) |
Where:
•aSRP ≡ Acceleration due to solar radiation pressure •S ≡ Mean solar flux at one astronomical unit (AU), defined as 1,358.0 W/m2(1) •AU ≡ Astronomical Unit (the distance from the Earth to the Sun), defined as 149,597,870.0 km •CR ≡ Coefficient of Reflectivity of the Spacecraft •ASRP ≡ SRP Area (the cross-sectional area incident to the Sun-Earth line) •m ≡ Mass of the Spacecraft •R ≡ Distance from the Spacecraft to the Sun •c ≡ Speed of light, defined as 299,792.458 km/s •U ≡ Unit vector from the Spacecraft to the Sun •ν ≡ Eclipse factor, where: oν = 0 if the Spacecraft is in shadow (umbra) oν = 1 if the Spacecraft is in sunlight o0 < ν < 1 if the Spacecraft is in penumbra(2) |
(1) Larson, W. J. and Wertz, J. R. Space Mission Analysis and Design (2nd Ed.), Microcosm Press, El Segundo, CA
(2) Equation 3-59, Page 76 of Wertz, James R., Spacecraft Attitude Determination and Control, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, MA
Note: The calculation of the eclipse factor (v) only considers shadows from the Spacecraft's current central body, except for the case where the central body is the Earth or Moon, in which case shadows from both the Earth and Moon are considered. When the central body is the Sun, the eclipse factor is always equal to 1.
Enabling Spherical SRP Modeling
To set up a Spacecraft using the spherical SRP calculation mode and specify the coefficient of reflectivity and SRP area, the following syntax can be used:
// To enable Spherical SRP (Spacecraft1.Propagator AsType RK89).ForceModel.SRP = 1; (Spacecraft1.Propagator AsType Integrator).ForceModel.SRPForceGeometry = 0; // 0 = Spherical
// Set coefficient of reflectivity and SRP Area Spacecraft1.Cr = 1.6; Spacecraft1.SRPArea = 2; // 2m^2 |
Note, users can perform higher fidelity SRP modeling through the use of a flat plate model that represents the geometry of your Spacecraft. For more information on flat plate models, see the Flat Plate Model page.
See Also
•ForceModel Properties and Methods
•ForceModel.SRP property
•Spacecraft.SRPArea property
•Spacecraft.Cr property